The Center for Computational Astrophysics executes research programs on systems ranging in scales from planets to cosmology, creating and using computational tools for data analysis and theory. It also supports, trains, and equips diverse members of the global astrophysics community and convenes events and workshops in New York City.
Featured News

A comprehensive set of simulations by Flatiron Institute astrophysicists and their colleagues revealed that magnetic fields are responsible for creating black holes with masses in a range previously thought to be largely off-limits.
Our Mission:
▪ Solve important, hard problems in computational astrophysics. Focus on problems that we at Flatiron are uniquely positioned to solve. ▪ Invent and propagate better data-analysis practices, analytical methods and computational methods for the global astrophysics community, with a focus on rigor. ▪ Develop, maintain and contribute to open-source software packages, open data and their communities. ▪ Create and support a community of astrophysics doers, learners and mentors in New York City and beyond. ▪ Train and launch diverse early-career researchers in astrophysics with unique capabilities in computational methods.
Groups


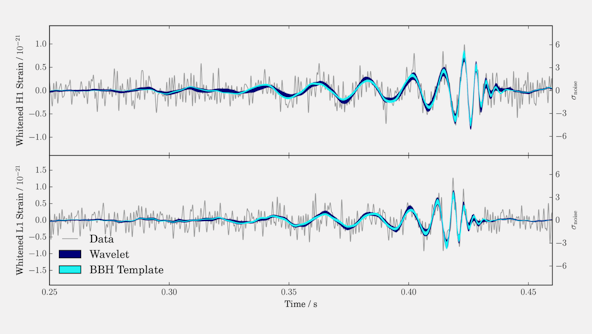

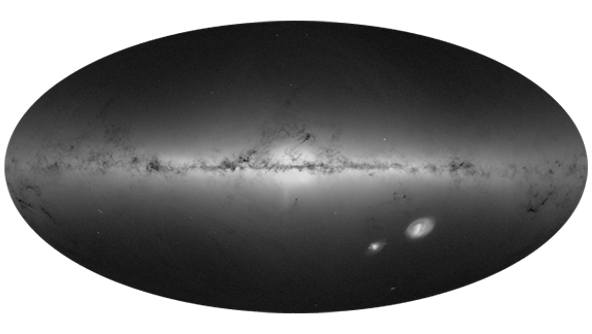

Collaborative Work

This collaboration aims to understand and determine the evolution and initial conditions of our universe, using observations via a Bayesian forward modeling approach.
- CCA
- | Columbia University
- | Lawrence Berkeley National Lab
- | Harvard University
- | Stockholm University
- | Institute D'Astrophysique de Paris
- | Université de Montreal
- | Princeton University
- | Carnegie Mellon University
- | Max-Planck Institute for Astrophysics
Upcoming Events
-
30 Fri -
Colloquium 3:00 - 4:00 p.m.
CCA Colloquium: Carl Louis Rodriguez
-
Colloquium 3:00 - 4:00 p.m.
-
06 Fri -
Colloquium 3:00 - 4:00 p.m.
CCA Colloquium: Aaron Smith
-
Colloquium 3:00 - 4:00 p.m.
-
18 Wed -
Workshop 9:00 a.m. - 5:30 p.m.
AGN & Energy Flows Workshop
-
Workshop 9:00 a.m. - 5:30 p.m.
-
20 Fri -
Colloquium 3:00 - 4:00 p.m.
CCA Colloquium: Eva Laplace
-
Colloquium 3:00 - 4:00 p.m.
-
27 Fri -
Colloquium 3:00 - 4:00 p.m.
CCA Colloquium: TBD
-
Colloquium 3:00 - 4:00 p.m.
-
06 Fri -
Colloquium 3:00 - 4:00 p.m.
CCA Colloquium: TBD
-
Colloquium 3:00 - 4:00 p.m.
-
13 Fri -
Colloquium 3:00 - 4:00 p.m.
CCA Colloquium: Diana Powell
-
Colloquium 3:00 - 4:00 p.m.
-
27 Fri -
Colloquium 3:00 - 4:00 p.m.
CCA Colloquium: TBD
-
Colloquium 3:00 - 4:00 p.m.
-
03 Fri -
Colloquium 3:00 - 4:00 p.m.
CCA Colloquium: Nora Shipp
-
Colloquium 3:00 - 4:00 p.m.
-
10 Fri -
Colloquium 3:00 - 4:00 p.m.
CCA Colloquium: Alice Shapley
-
Colloquium 3:00 - 4:00 p.m.
Event Videos
View all videos →
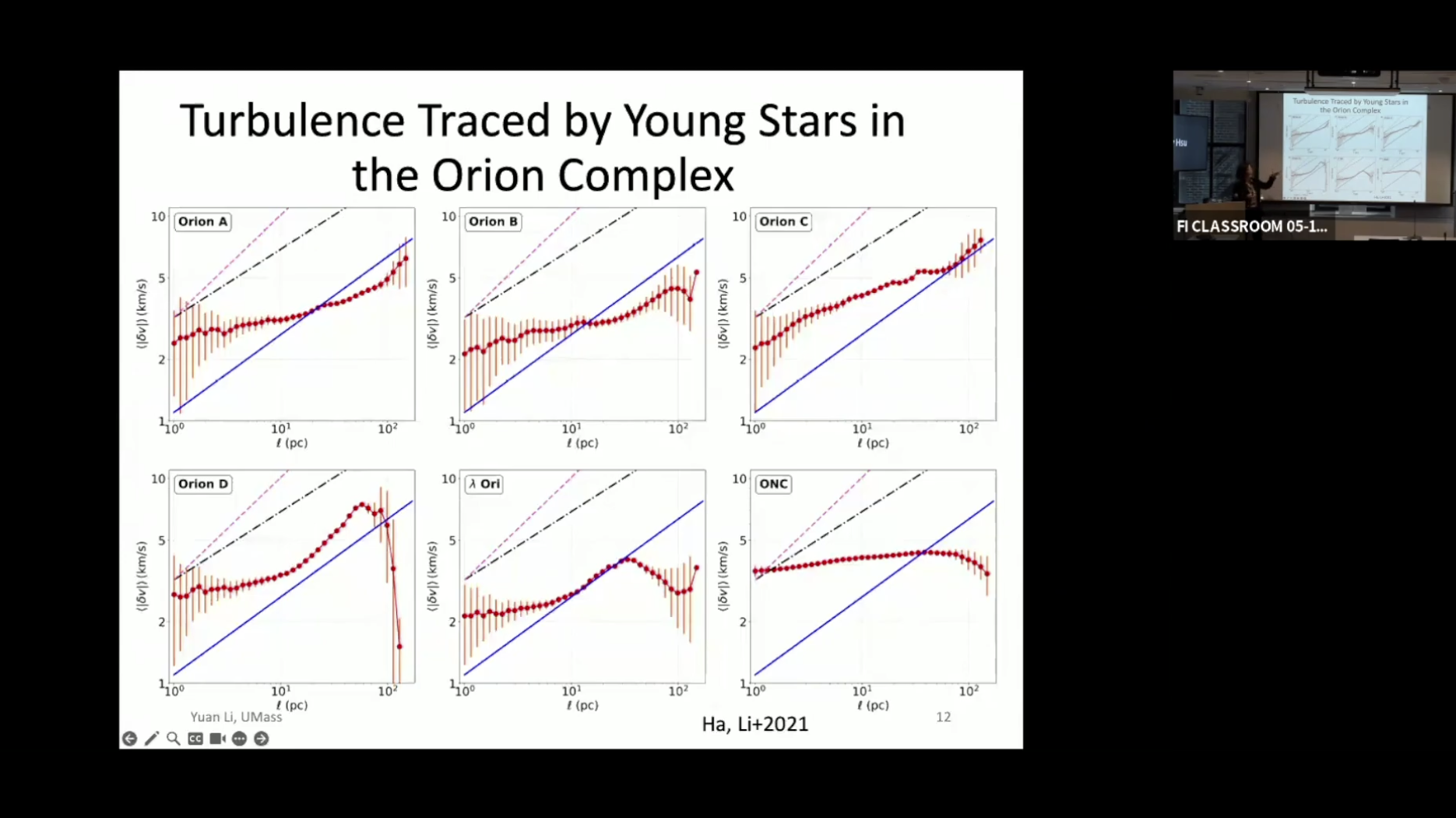
Yuan Li: Turbulence Across Cosmic Scales: From the Interstellar to Intracluster Medium
Read More
Kevin Burdge: From 7 minutes to 70000 years: the Renaissance of compact objects in binary (and triple) systems
Read More
Jason Sanders: A Biased History of our Galaxy
Read More
Neal Dalal: AGN HBT OMG
Read More
Publications
Cosmological constraints from non-Gaussian and nonlinear galaxy clustering using the SimBIG inference framework
The standard ΛCDM cosmological model predicts the presence of cold dark matter, with the current accelerated expansion of the Universe…
Nature AstronomyListening to the noise: Blind Denoising with Gibbs Diffusion
In recent years, denoising problems have become intertwined with the development of deep generative models. In particular, diffusion models are…
Proceedings of Machine Learning ResearchFishing for Planets: A Comparative Analysis of EPRV Survey Performance in the Presence of Correlated Noise
With dedicated exoplanet surveys underway for multiple extreme-precision radial velocity (EPRV) instruments, the near-future prospects of RV exoplanet science are…
The Astronomical JournalDirector
Software

Astrometry.net
If you have astronomical imaging of the sky with celestial coordinates you do not know—or do not trust—then Astrometry.net is for you. Input an image and we'll give you back astrometric calibration meta-data, plus lists of known objects falling inside the field of view.

celerite
celerite is a library for fast and scalable Gaussian Process (GP) Regression in one dimension with implementations in C++, Python, and Julia.
DAFT
Daft is a Python package that uses matplotlib to render pixel-perfect probabilistic graphical models for publication in a journal or on the internet.

emcee
emcee is an extensible, pure-Python implementation of Goodman & Weare's Affine Invariant Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) Ensemble sampler. It's designed for Bayesian parameter estimation.

EXP
The EXP C++ library is an efficient N-body simulation toolkit that implements basis-function methods using hybrid CPU and GPU code alongside Python bindings.

Gala
Galactic Dynamics is the study of the formation, history, and evolution of galaxies using the orbits of objects — numerically-integrated trajectories of stars, dark matter particles, star clusters, or galaxies themselves.

George
George is a fast and flexible Python library for Gaussian Process Regression. It capitalizes on the Hierarchical Off-Diagonal Low-Rank formalism to make controlled approximations for fast execution.

MESA
MESA is a robust suite of open-source, robust, efficient, thread-safe libraries extensively used in computational stellar astrophysics.

Pyia
Pyia is a Python package for interacting and working with data from the Gaia Mission.

smolgp
State Space Models for O(Linear/Log) Gaussian Processes is a scalable & GPU-parallel Gaussian Processes in JAX using the state space representation, particularly suited for integrated measurements and multiple datasets

STARRY
starry enables the computation of fast and precise light curves for various applications in astronomy: transits and secondary eclipses of exoplanets, light curves of eclipsing binaries, rotational phase curves of exoplanets, light curves of planet-planet and planet-moon occultations, and more.